Table of Contents
Have you heard about ecological pyramids? An ecological pyramid is a representation of the relationships between living things at certain levels. To understand more about it, read this article to the end!
What Is an Ecological Pyramid?
An ecological pyramid, also known as a trophic pyramid, food pyramid, or energy pyramid, is a concept of the relationships between living things introduced by Charles Elton in 1927. This pyramid is formed from the amounts of energy, people, and biomass, which are then arranged in a pyramid.
Producers usually occupy the bottom of the pyramid. Then, the pyramid continues to primary consumers, secondary consumers, and tertiary consumers at the top.
The ecological pyramid also explains who eats whom and the relationships among living things, such as eagles as predators and mice as prey. Not only that, this pyramid also illustrates the flow of energy that occurs from producers to tertiary consumers.
Read also: What Is Zero Waste? Learn the Benefits and How to Apply It
Types of Ecological Pyramids
Generally, there are three types of ecological pyramids that you need to know, including:
1. Biomass Pyramid
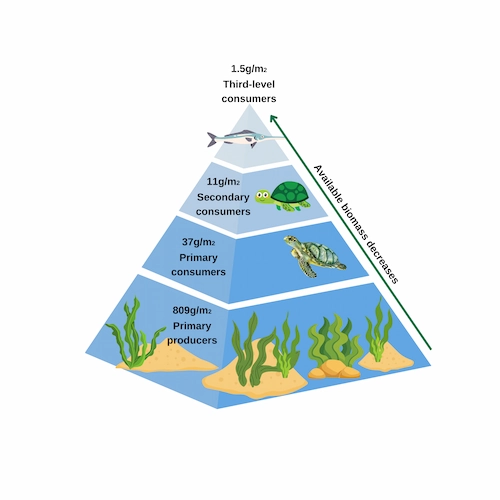
In a biomass pyramid, each level accounts for the amount of biomass produced. Most biomass pyramids are upright. However, there are also marine biomass pyramids where the widest part is at the top, occupied by zooplankton.
2. Pyramid of Numbers

The following example is the pyramid of numbers. This pyramid shows the number of organisms at each level. Usually, this pyramid is upright, though inverted pyramids also exist.
For example, the bottom level is occupied by 1 million grasses; above that, 300,000 herbivorous insects; then 100,000 small insect predators; and at the top, one eagle.
What distinguishes inverted and upright pyramids of this type is their base. Upright pyramids have more producers at the bottom.
Meanwhile, the bottom of an inverted pyramid is occupied by a small number of producers. On the other hand, the top has a large population.
3. Energy Pyramid
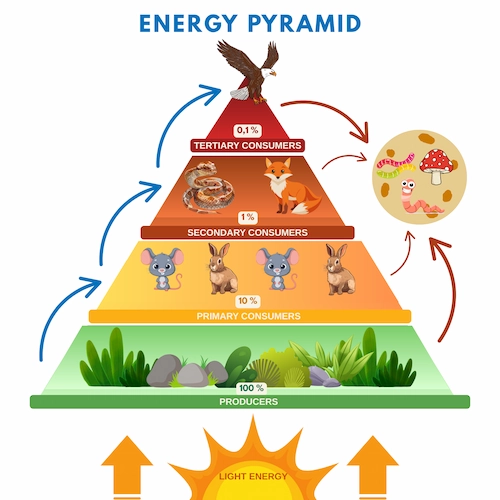
This pyramid is the only ecological pyramid that stands upright because the energy in the food chain always flows in one direction. The bottom of the pyramid has the most energy, and the top has the least energy.
Then, as the level increases, some energy is released into the environment. This is because not all parts of an organism are eaten, for example, bones and roots. Then, living things generally produce waste (feces), which is also absorbed by the environment.
Other forms of energy include heat produced by the respiratory process and urine, a product of the body’s metabolism.
Characteristics of the Ecological Pyramid
Ecological pyramids usually have several characteristics, such as:
- Organisms that depend on the same type of food source will be at the same level. For example, grasshoppers and caterpillars are primary consumers because they eat grass (producers).
- This pyramid contains 2–4 levels.
- The concept of the ecological pyramid is based on predator-prey relationships.
- Organisms occupy the lowest level of the pyramid with the largest populations.
- The main predators will be at the top of the pyramid and have smaller populations than the levels below them.
- If the food chain is disrupted, the entire biological pyramid will be disrupted, and the environment will be seriously affected.
Read also: 10 Benefits of Protected Forest for All Living Creatures
How to Protect Ecosystems and the Environment

As explained earlier, the destruction of the food chain can damage the entire biological pyramid. Therefore, protecting the environment is crucial to ensuring the ecosystem continues to function optimally. Here are some ways to protect the ecosystem that you can try:
1. Conserving Water
Water is an important natural resource for living things, and its availability affects the survival of the ecosystem. Therefore, it is advised to conserve water by fixing leaks to avoid waste and using it wisely.
2. Planting Trees
The next thing you can do is participate in tree planting initiatives. Trees play an important role in providing habitat for many plant and animal species. In addition, trees can prevent landslides and floods, allowing the ecosystem to continue functioning.
3. Treating Waste Properly
Waste can pollute the environment and disrupt the ecosystem chain. Therefore, we must manage waste properly and reduce its production. Some ways to do this include the 3Rs (reduce, reuse, recycle), composting, and sorting waste by type.
4. Protecting Flora and Fauna
Currently, many forests are being cleared for mining and palm oil plantations. This undoubtedly contributes to the extinction of the natural habitats of flora and fauna in Indonesia.
As a Warga Asri who cares about the Earth, you can contribute to protecting flora and fauna by avoiding destroying animal habitats and nests when exploring nature, not supporting animal trafficking (such as keeping protected animals), and reporting cases of animal exploitation to the authorities.
5. Increasing Knowledge and Awareness
Education and awareness of the importance of ecosystems are essential, as they help you make meaningful contributions to the environment.
So, stay updated on environmental issues, green initiatives, and ongoing conservation projects. Then, make sure your friends, family, and colleagues also raise their awareness about protecting the environment.
If you want to contribute to the Earth and deepen your understanding of environmental issues, you can join Indonesia Asri.
With Indonesia Asri, you can participate in various #AksiAsri and exciting challenges that educate and have a positive impact on the environment. You will also continue to receive new information related to environmental issues.
Register now and help protect the environment for the sustainability of Earth’s ecosystems!
Read also: 10 Efforts That Can Be Made to Overcome Environmental Pollution










